レーベンシュタイン距離 を計算する
"文字列の類似度"を計算するアルゴリズムである”レーベンシュタイン距離”について以下に記載します。
レーベンシュタイン距離(英語: Levenshtein distance)は、
二つの文字列がどの程度異なっているかを示す距離の一種である。編集距離(英語: edit distance)とも呼ばれる。
具体的には、1文字の挿入・削除・置換によって、一方の文字列をもう一方の文字列に変形するのに必要な手順の最小回数として定義される。名称は、1965年にこれを考案したロシアの学者
ウラジーミル・レーベンシュタイン (露: Влади́мир Левенште́йн) にちなむ。
レーベンシュタイン距離は、同じ文字数の単語に対する置換編集に使われているハミング距離の一般化であると見なすことが可能である。レーベンシュタイン距離の更なる一般化として、例えば一回の操作で二文字を変換する等の方法が考えられる。
[引用元: レーベンシュタイン距離 - Wikipedia]
c# による実装例を以下に記載します。
[環境]
|
| コンパイラ : |
Visual Studio 2013 pro., |
|
|
| OS : |
Windows8.1 64bit, |
|
|
using System;
namespace LevenshteinCs
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string str1 = "apple";
string str2 = "maple";
// "レーベンシュタイン距離" を計算
int distance = GetLevenshtein(str1, str2);
// 計算結果をコンソールへ出力
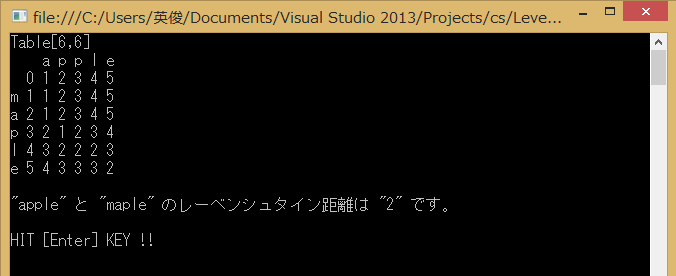
Console.WriteLine("\n\"{0}\" と \"{1}\" のレーベンシュタイン距離は \"{2}\" です。", str1, str2, distance);
// [Enter] 入力待ち
Console.Write("\nHIT [Enter] KEY !! ");
Console.ReadLine();
}
// "レーベンシュタイン距離" を計算
private static int GetLevenshtein(string s1, string s2)
{
string str1 = " " + s1;
string str2 = " " + s2;
int distance = 0;
int[,] table = new int[str2.Length, str1.Length];
// テーブル初期化
for (int i = 0; i < str1.Length; ++i)
{
table[0, i] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < str2.Length; ++i)
{
table[i, 0] = i;
}
// 計算
for (int y = 1; y < str2.Length; ++y)
{
for (int x = 1; x < str1.Length; ++x)
{
table[y, x] = min(table[y - 1, x] + 1, table[y, x - 1] + 1, table[y - 1, x - 1] + (str1[x] != str2[y] ? 1 : 0));
}
}
print2DArray(str1, str2, table);
// これが "レーベンシュタイン距離" の算出結果
distance = table[str2.Length - 1, str1.Length - 1];
return distance;
}
private static int min(int p1, int p2, int p3)
{
return Math.Min(p1, Math.Min(p2, p3));
}
// 計算結果の二次元テーブルをコンソールへ出力
private static void print2DArray(string s1, string s2, int[,] table)
{
Console.WriteLine("Table[{0},{1}]", table.GetLength(0), table.GetLength(1) );
System.Diagnostics.Trace.WriteLine("x=" + table.GetLength(0) + ", y=" + table.GetLength(1));
Console.Write(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < s1.Length; ++i) {
Console.Write("{0} ",s1[i]);
}
Console.WriteLine();
for (int y = 0; y < table.GetLength(0); ++y)
{
Console.Write("{0} ", s2[y]);
for (int x = 0; x < table.GetLength(1); ++x)
{
Console.Write(table[y, x] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
}
[実行結果]
c++ による実装例を以下に記載します。
[環境]
|
| コンパイラ : |
Visual Studio 2013 pro., |
|
|
| OS : |
Windows8.1 64bit, |
|
|
C/C++ の実装では日本語を含むマルチバイト文字を使用できるように、UNICODE を使用して、
ロケールを指定したうえでワイドキャラクタ、ワイドストリング(wcout, wchar, wstring) などを使って実装しています。
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <string> // string
#include <algorithm> // min
#include <vector> // vector
#include <locale> // locale
#include <crtdbg.h> // _RPT2
using namespace std;
// 計算結果の二次元テーブルをコンソールへ出力
void print2DArray(wstring s1, wstring s2, vector<vector<int>>& table)
{
cout << "Table[" << table.size() << "][" << ((vector<int>)(table[0])).size() << "]" << endl;
_RPT2(_CRT_WARN, "x=%d, y=%d\n", table.size(), (vector<int>(table[0])).size());
cout << " ";
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); ++i) {
wcout << s1[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (size_t y = 0; y < table.size(); ++y)
{
wcout << s2[y] << " ";
for (size_t x = 0; x < ((vector<int>)(table[0])).size(); ++x)
{
cout << table[y][x] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
// "レーベンシュタイン距離" を計算
int GetLevenshtein( wstring s1, wstring s2)
{
wstring str1 = L" " + s1;
wstring str2 = L" " + s2;
int distance = 0;
vector<vector<int>> table( str2.length(), vector<int>(str1.length()));
// テーブル初期化
for (size_t i = 0; i < str1.length(); ++i)
{
table[0][i] = i;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < str2.length(); ++i)
{
table[i][0] = i;
}
// 計算
for (size_t y = 1; y < str2.length(); ++y)
{
for (size_t x = 1; x < str1.length(); ++x)
{
table[y][x] = min({table[y - 1][x] + 1, table[y][x - 1] + 1, table[y - 1][x - 1] + (str1[x] != str2[y] ? 1 : 0)});
}
}
print2DArray(str1, str2, table);
// これが "レーベンシュタイン距離" の算出結果
distance = table[str2.length() - 1][str1.length() - 1];
return distance;
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
// ロケール設定 : ロケールを日本に設定
locale lw("Japanese_Japan");
locale::global(lw);
wcout.imbue(lw);
// 距離を計算する2つの文字列
wstring str1 = L"apple";
wstring str2 = L"maple";
// レーベンシュタイン距離 を計算
int distance = GetLevenshtein(str1, str2);
// 計算結果をコンソールへ出力
wcout << L"\n\"" << str1 << L"\" と \"" << str2 << L"\" のレーベンシュタイン距離は \"" << distance << L"\" です。" << endl;
// [Enter] 入力待ち
cout << "\nHIT [Enter] Key !! ";
{
string str;
getline(cin, str);
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
[実行結果]

Python による実装例を以下に記載します。
[環境]
|
| 言語 : |
Python, |
3.10.7 |
|
| OS : |
Windows 11 home, |
22H2 |
|
def levenshtein(s1, s2):
n = len(s1)
m = len(s2)
table = [[0] * (m + 1) for _ in range(n + 1)]
for i in range(n + 1):
table[i][0] = i
for j in range(m + 1):
table[0][j] = j
for i in range(1, n+1):
for j in range(1, m+1):
a = table[i][j-1] + 1
b = table[i-1][j] + 1
cost = 0 if s1[i-1] == s2[j-1] else 1
c = table[i-1][j-1] + cost
table[i][j] = min(a, b, c)
print(*table, sep='\n')
return table[n][m]
if __name__ == "__main__":
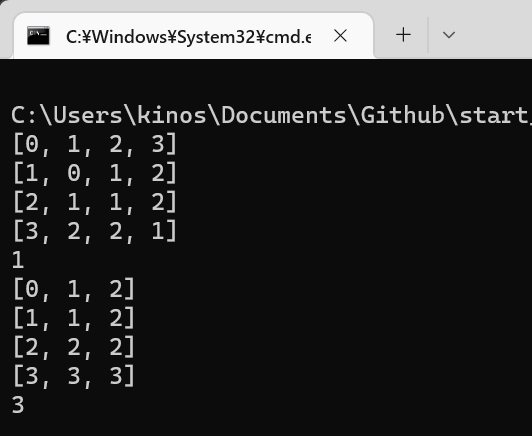
print(levenshtein('うさぎ', 'うなぎ'))
print(levenshtein('うさぎ', 'ねこ'))
[実行結果]
本ページの情報は、特記無い限り下記 MIT ライセンスで提供されます。
The MIT License (MIT)
Copyright © 2015-2022 Kinoshita Hidetoshi
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
SOFTWARE.
- 日経ソフトウェア 2014年3月号 12~13ページ、第4回 プログラミング入門塾
-
レーベンシュタイン距離(wiki)
- 日経ソフトウェア 2023年1月号 特集1「絶対に知っておきたい アルゴリズム10選」

