std::thread (c++11)
std::thread
は boost::thread から標準に採用されたライブラリです。
C++03 ではスレッドライブラリがなかったので Win32 や pthread を使う必要がありました。Win32 の _beginthread を使用した場合はクラスのメソッドを呼ぶ場合に static
なメソッドなどをいったん間にかませる必要があるのですが、この std::thread はこの手順が不要でクラスメソッドを一発起動できて便利です。
類似の機能として std::jthread, std::async などがあります。
C++標準には、非同期処理を行う方法に std::thread, std::jthread,
std::async の3つがあります。
最初にこの3つについて概要を記載します。
🦊 参考(選び方の目安)
|
目的 |
推奨される選択肢 |
| スレッドを完全に制御したい |
std::thread |
| 安全にスレッドを扱いたい |
std::jthread |
| 戻り値が必要な非同期処理を簡単に書きたい |
std::async |
🧵 std::thread
| 特徴 |
最も基本的なスレッド。スレッドの生成と管理を自分で行う。 |
| 利点 |
細かい制御が可能(スレッドのライフサイクル、優先度など) |
| 注意点 |
-
join() や
detach()
を忘れると未定義動作になる
- スレッド終了の管理が手動で面倒
|
| 使いどころ |
スレッドの寿命や動作を細かく制御したいとき |
🌿 std::jthread
| 特徴 |
std::thread
の改良版。スレッド終了時に自動で join() してくれる |
| 利点 |
- リソースリークの心配が少ない(RAIIで自動管理)
stop_token によるキャンセル機構が組み込まれている
|
| 注意点 |
- C++20以降が必要
- 一部の環境ではまだ完全にサポートされていないかも
|
| 使いどころ |
スレッドのキャンセルや自動管理が欲しいとき。
C++20 を使えるなら std::thread
よりこちらの方が安全。 |
⚡ std::async
| 特徴 |
関数を非同期に実行し、std::future
で結果を取得。 |
| 利点 |
- 戻り値を簡単に取得できる
- スレッド管理が不要
- リソースリークの心配が少ない(RAIIで自動管理)
|
| 注意点 |
-
実行ポリシー
(std::launch::async or
std::launch::deferred) に注意。実装依存でスレッドが作られないこともある。
-
std::launch::async を使って新しいスレッドを起動した場合、future
の get()
や wait() を呼ばずに future
を破棄すると、スレッドがバックグラウンドで動いたままになる可能性がある。
-
std::launch::deferred の場合、スレッドを作成しない。また、future
の get()
を呼ばないと関数自体が実行されない。
|
| 使いどころ |
「関数を非同期に呼び出して結果を待ちたい」ようなシンプルなケースに最適 |
以下、本ページでは std::thread について記載します。
まずは一番シンプルな実装から試します。
[評価環境]
|
| コンパイラ : |
Visual Studio 2019 pro., |
Version 16.6.0 |
|
| OS: |
Windows10 home, |
Version 1909 |
|
[プログラムソース]
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <chrono>
using namespace std;
void PrintHello()
{
const size_t RepeatCount = 5 ;
for ( size_t i=0; i<RepeatCount; ++i ){
cout << "Hello " << endl;
this_thread::sleep_for( chrono::milliseconds(500) );
}
}
void PrintWorld()
{
const size_t RepeatCount = 5 ;
for ( size_t i=0; i<RepeatCount; ++i ){
cout << "World! " << endl;
this_thread::sleep_for( chrono::milliseconds(500) );
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
thread thr_hello(PrintHello);
thread thr_world(PrintWorld);
thr_hello.join();
thr_world.join();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
引数付きの関数実行を同じく std::thread を使ったマルチスレッドで実行する方法を記載します。
thread
には関数ポインタを渡すのですが、オーバーロードした関数がある場合の記載方法が難しいのでこれについても記載します。結論から言うとキャストで関数詳細情報を記載すればできるようです。
同様に、lambda 式 による実装も記載します。
[評価環境]
|
| コンパイラ : |
Visual Studio 2012 Update3 |
|
|
| OS: |
Windows8 64bit |
|
|
[プログラムソース]
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <chrono>
#include <string>
#include <tchar.h>
using namespace std;
void PrintString( const char* str )
{
const size_t RepeatCount = 5 ;
for ( size_t i=0; i<RepeatCount; ++i ){
cout << str << endl;
this_thread::sleep_for( chrono::milliseconds(500) );
}
}
#if 0
void PrintString( const string str )
{
const size_t RepeatCount = 5 ;
for ( size_t i=0; i<RepeatCount; ++i ){
cout << str << endl;
this_thread::sleep_for( chrono::milliseconds(500) );
}
}
#endif
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
{
#if 1
thread thr_hello( PrintString, "Hello " );
thread thr_world( PrintString, "World! ");
thread thr_space( PrintString, "Space ") );
#endif
#if 0
thread thr_hello( static_cast<void(*)(const char*)>(PrintString), "Hello " );
thread thr_world( static_cast<void(*)(const char*)>(PrintString), "World! ");
thread thr_hide ( static_cast<void(*)(const string)>(PrintString), string("hide"));
thread thr_space( std::bind(static_cast<void(*)(const char*)>(PrintString), "Space ") );
#endif
#if 0
thread thr_hello([=]{
PrintString("Hello ");
});
thread thr_world([=]{
PrintString(string("World! "));
});
thread thr_space([=]{
PrintString("Space ");
});
#endif
thr_hello.join();
thr_world.join();
thr_space.join();
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
クラスメンバ関数をスレッド起動する方法です。
クラスメソッドは第一引数にインスタンス (this) が必要です。このため下記サンプルでは &hello,
&world を引数で渡す必要があります。
[評価環境]
|
| コンパイラ : |
Visual Studio 2012 Update3 |
|
|
| OS: |
Windows8 64bit |
|
|
[プログラムソース]
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <thread>
#include <chrono>
using namespace std;
class PrintMessage {
private:
const string strMessage_ ;
public:
PrintMessage( string strMessage ) : strMessage_(strMessage)
{
}
void run()
{
const size_t RepeatCount = 5 ;
for ( size_t i=0; i<RepeatCount; ++i ){
std::cout << strMessage_ << endl;
this_thread::sleep_for( chrono::milliseconds(500) );
}
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
PrintMessage hello("Hello ");
PrintMessage world("World! ");
thread thr_hello( &PrintMessage::run, &hello );
thread thr_world( &PrintMessage::run, &world );
thr_hello.join();
thr_world.join();
}
クラスメンバ関数をスレッド起動する方法です。
クラスメソッドなので第一引数にインスタンス(this)が必要です。このため下記サンプルでは
this を引数で渡しています。
[評価環境]
|
| コンパイラ : |
g++ (Ubuntu 13.3.0-6ubuntu2~24.04), |
13.3.0 |
|
| OS: |
Ubuntu 24.04 (WSL), |
|
|
[プログラムソース] thread_01.cpp
#include <iostream> // cout, endl
#include <string> // string
#include <thread> // thread, this_thread::sleep_for
#include <chrono> // chrono::millisecond
/// メッセージを出力するクラス
class PrintMessage {
private:
const std::string strMessage_ ;
std::thread worker_ ;
public:
PrintMessage( std::string strMessage ) : strMessage_(strMessage)
{
worker_ = std::thread( &PrintMessage::run, this);
}
~PrintMessage() {
if (worker_.joinable()) {
worker_.join();
}
}
void run()
{
const size_t RepeatCount = 5 ;
for ( size_t i=0; i<RepeatCount; ++i ){
std::cout << strMessage_ << std::endl;
std::this_thread::sleep_for( std::chrono::milliseconds(500) );
}
}
void join()
{
worker_.join();
}
};
/// メイン関数
int main()
{
// メンバ関数をマルチスレッドで実行(クラス内部からの起動)
{
PrintMessage hello("Hello ");
PrintMessage world("World! ");
hello.join();
world.join();
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
ビルドおよび実行結果:
$ g++ -std=c++11 -Wall -Wextra -Wpedantic -pthread -O2 thread_01.cpp -o thread_01.out
$ ./thread_01.out
Hello
World!
Hello
World!
Hello
World!
Hello
World!
Hello
World!
$
ビルドオプション説明:
| オプション |
説明 |
| -std=c++11 |
C++11 標準でコンパイルします。言語機能(構文・ライブラリ仕様)が C++11 準拠になります。 |
| -Wall |
一般的な警告群を有効にします。コード品質の初期チェックに有用です。 |
| -Wextra |
-Wall に含まれない追加の警告を有効にします。未使用パラメータなどを検出します。 |
| -Wpedantic |
規格に厳格に従っていない拡張や非標準的記法を警告します。移植性を高めたい場合に有効です。 |
| -pthread |
POSIX threads
のサポートを有効にし、スレッド関連のライブラリをリンクします。単に -lpthread をリンクするだけでなく、コンパイル時にスレッド対応(スレッドセーフな定義など)を有効にするフラグです。スレッド/ミューテックスなどを使うプログラムでは必須に近いオプションです(Linux)。 |
| -O2 |
最適化レベル 2 を指定します。実行速度向上のための最適化を行うが、"-O3" よりは穏やかで安定的な設定です。デバッグ時は
"-g -O0"
を推奨します。 |
thread_01.cpp を Lambda 式による実装へ変更した例を以下で紹介します。
this をキャプチャーする、ことに気を付けるぐらいです。
this 無しでも thread
作成はできますが、下記例ではスレッドからクラスメンバー(PrintMessage::strMessage_)をアクセスできずビルドエラーになります。クラスメンバーへのアクセス不要なら
this のキャプチャーは不要です。
[プログラムソース] thread_02.cpp
#include <iostream> // cout, endl
#include <string> // string
#include <thread> // thread, this_thread::sleep_for
#include <chrono> // chrono::millisecond
/// メッセージを出力するクラス
class PrintMessage {
private:
const std::string strMessage_ ;
std::thread worker_ ;
public:
PrintMessage( std::string strMessage ) : strMessage_(strMessage)
{
worker_ = std::thread( [this]() {
const size_t RepeatCount = 5 ;
for ( size_t i=0; i<RepeatCount; ++i ){
std::cout << strMessage_ << std::endl;
std::this_thread::sleep_for( std::chrono::milliseconds(500) );
}
} );
}
~PrintMessage() {
if (worker_.joinable()) {
worker_.join();
}
}
void join()
{
worker_.join();
}
};
/// メイン関数
int main()
{
// メンバ関数をマルチスレッドで実行(クラス内部からの起動)
{
PrintMessage hello("Hello ");
PrintMessage world("World! ");
hello.join();
world.join();
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
ビルドおよび実行結果:
$ g++ -std=c++11 -Wall -Wextra -Wpedantic -pthread -O2 thread_02.cpp -o thread_02.out
$ ./thread_02.out
Hello
World!
Hello
World!
Hello
World!
Hello
World!
Hello
World!
$
一時停止状態のシステムスレッドを作成してみます。
すなわち、スレッドで何かを処理する時が来たらすぐに開始できるようにあらかじめスレッドを作成しておき、作成のスレッドのオーバーヘッドによる遅延を回避する例です。または、実行開始前にスレッドに何かしらのせえっていを行う必要があるため一時停止状態のスレッドを作成する場合もあるでしょう。
スレッドを一度だけ一時停止状態にしたい場合、void future を用いるのが妥当な選択です。この技法の要点を以下に示します。
[評価環境]
|
| コンパイラ : |
Visual Studio 2019 pro., |
Version 16.3.10 |
|
| OS : |
Windows10 home, |
Version 1909 |
|
[プログラムソース]
#include <iostream>
#include <thread> // std::thread
#include <future> // std::async
using namespace std;
int react(int count)
{
cout << "Start react()." << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::milliseconds(1000));
}
cout << "Finish react()." << endl;
return 1;
}
int main()
{
promise<void> p;
int wait_count = 5;
thread t([=, &p]
{
p.get_future().wait(); // p.set_value() の実行まで待機
return react(wait_count); // react() を実行
});
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::seconds(1)); // 何か・・・をしてから、
p.set_value(); // スレッドを起動します。
cout << "Waiting..." << endl;
t.join();
cout << "Confirmed termination of react()." << endl;
}
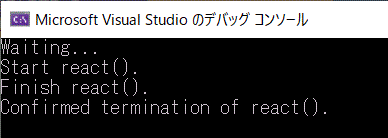
[実行結果]
本ページの情報は、特記無い限り下記 MIT ライセンスで提供されます。
The MIT License (MIT)
Copyright © 2013 Kinoshita Hidetoshi
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
SOFTWARE.
